



|



|





|

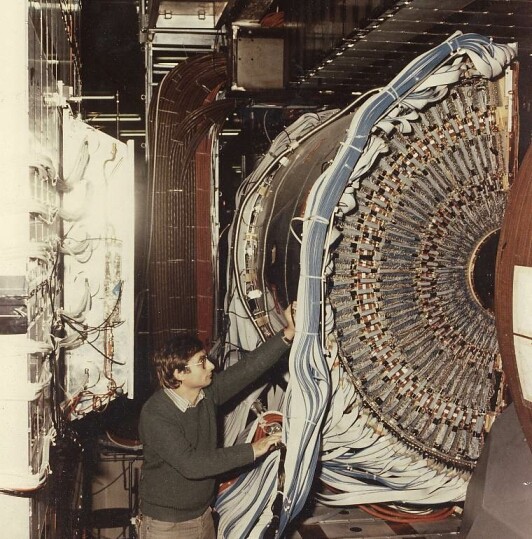
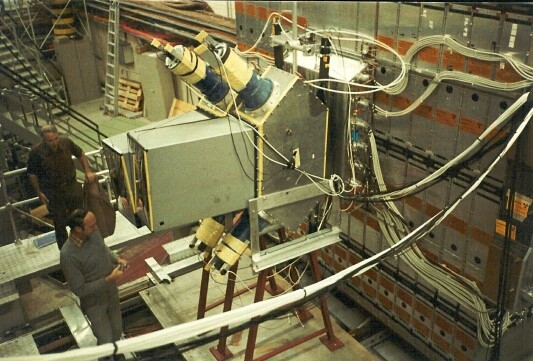
The Intersecting Storage Rings
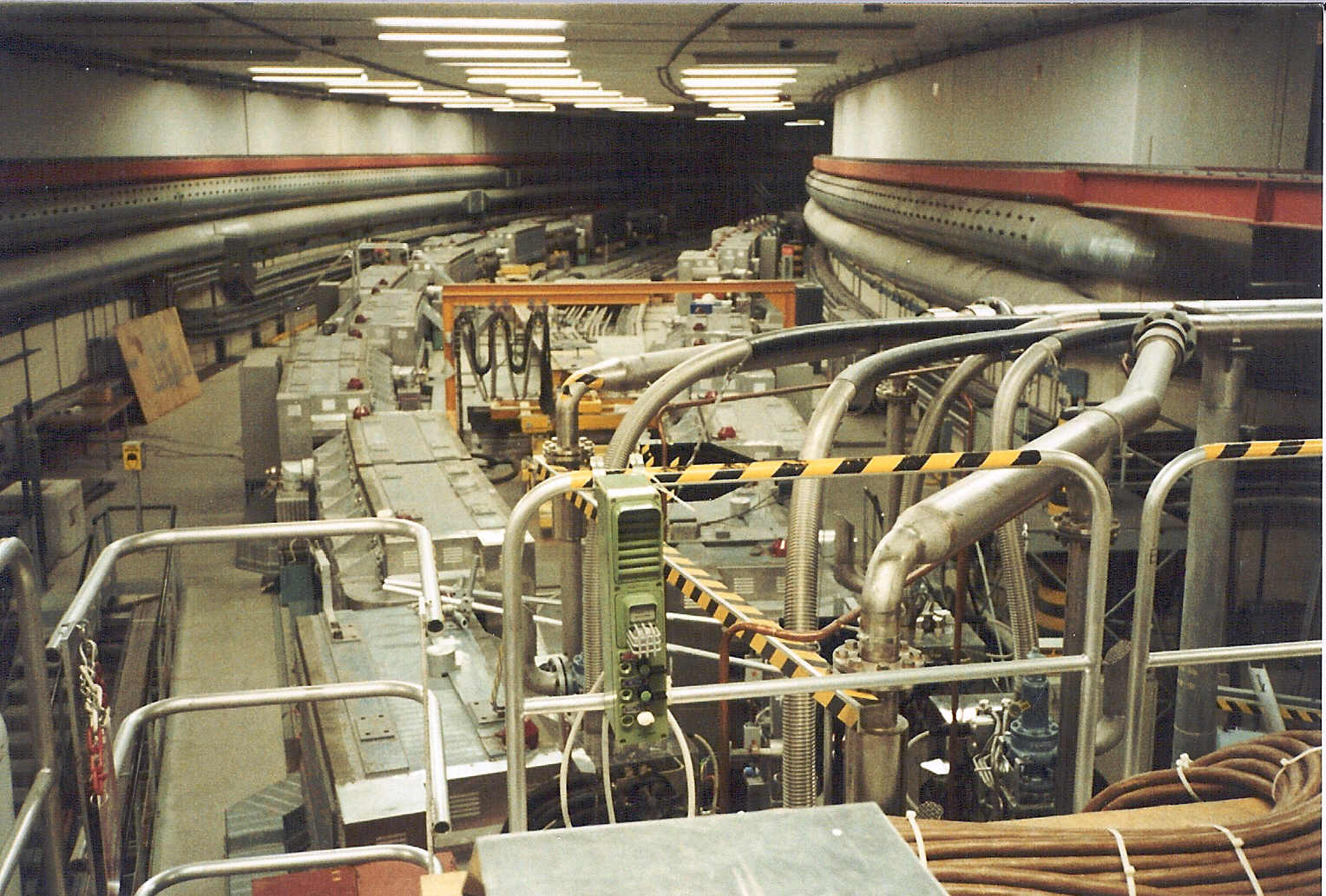
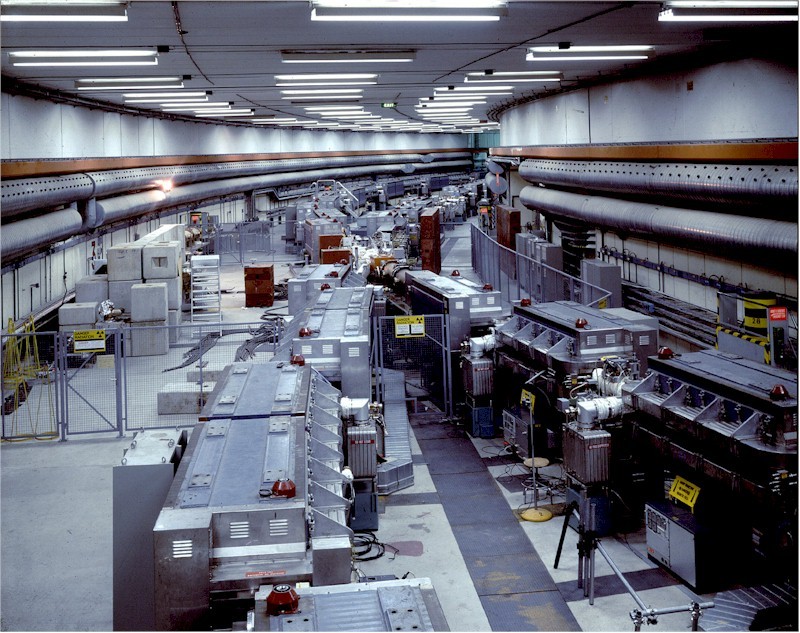
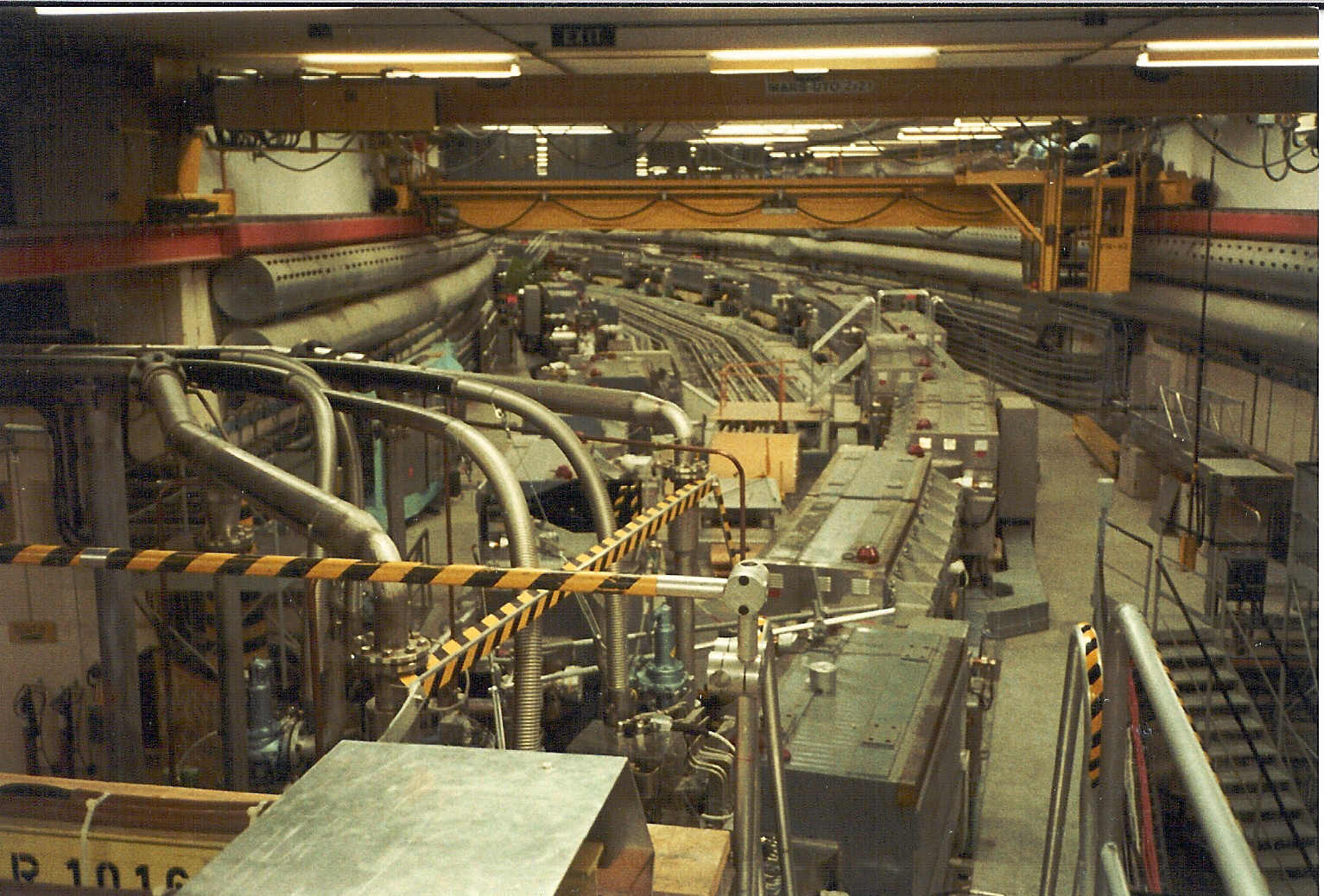
The Intersecting Storage Ring (ISR) was the worlds first high-energy hadron collider but as the name indicates
it was not an accelerator since the particles were accelerated by the CERN Proton Synchrotron (PS). The
protons (but also anti-protons, deuterium and alpha-particles) were brought from the PS to the ISR via two
transfer tunnels to the two 940 m long storage rings in the ISR. The hadrons could be brought into
collision at 8 intersection points around the rings. The maximum collision energy obtained was 63 GeV and this
was a considerably higher value than at previous fixed-target machines. Unfortunately the discovery potenial
of this unique machine was not used due to small low-budget experiments which did not cover a large enough
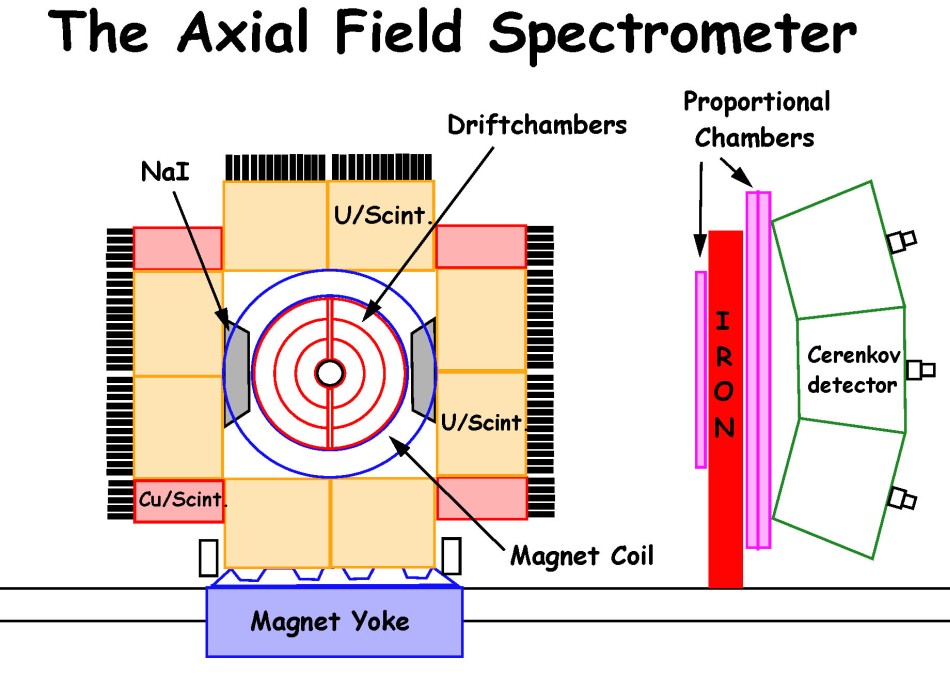
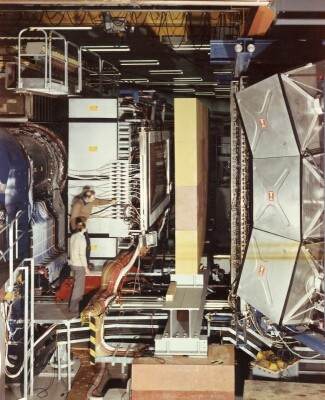
solid angle and it was not until the end of its lifetime that large experiments such as the AFS were carried out.
Responsible for the content of this page is
Vincent Hedberg
<